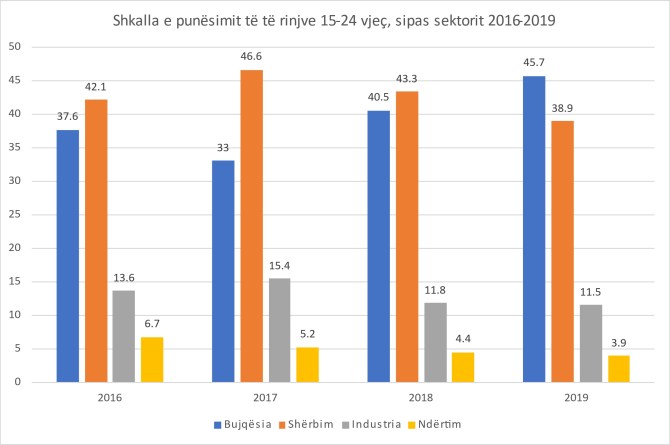
Agriculture is the sector with the lowest productivity in the economy, but in recent years, the share of young people employed in this sector has been increasing.
According to official INSTAT data, in 2019, about 46% of employees in the 15-24 age group were in the agricultural sector. The share of agriculture in youth employment during a year increased by 5.2 percentage points, while compared to 2016 increased by about 9 percentage points.
In contrast, youth employment in the higher productivity sectors fell. In the services sector were activated 40% of young people employed with a decrease of 4.4 percentage points compared to 2018 and over 2 percentage points compared to 2016.
The industry sector contributed 11.5% to the total employment of young people aged 15-24, with a slight decrease, 0.3 percentage points compared to 2018.
Only 3.9% of the total employees worked in the construction sector, with a decrease of 0.5 percentage points compared to 2018 and 2.8 percentage points compared to 2016. Although the construction sector grew rapidly in these four years lastly, he has not become attractive to young people.
Although the agricultural sector is the main contributor to employment and GDP in official statistics, it has the lowest productivity in the Region and beyond, while food imports in 2020 were 3 times higher than the sector’s exports.
Despite the expansion of exports, agriculture continues to be the least productive sector of the economy, and the increase in sales revenues is going more to supply chains than to producers. In the last quarter of 2020, the average gross monthly salary in agriculture was about 32 thousand ALL, or 40% lower than the national average salary. According to a study by the World Food Program (FAO), most farms in the country, those with an area of 1 hectare, result in losses and produce only for self-consumption.
Albania’s economy is dominated by agriculture which, although with primitive development, non-mechanized, fragmented and lack of high productivity accounted for 19.3 percent of total Gross Domestic Product in 2020, while in Europe the agricultural sector occupied only 1 , 3 percent of total GDP, according to Eurostat data.
Despite the chaotic developments in the agricultural sector due to high land fragmentation and lack of funding, the sector is seen as having the potential to increase exports. Favorable climate, experience in cultivation and increased external demand have put sales in a steady trend. Last year, the export of fresh vegetables dominated by tomatoes and cucumbers, reached 8.8 billion ALL, or 72 million euros with an annual increase of 13.3%.